Despite the proven lifesaving benefit of antibiotics for children with this inherited blood disorder, only 18 percent receive them.
4:00 PM
Author |
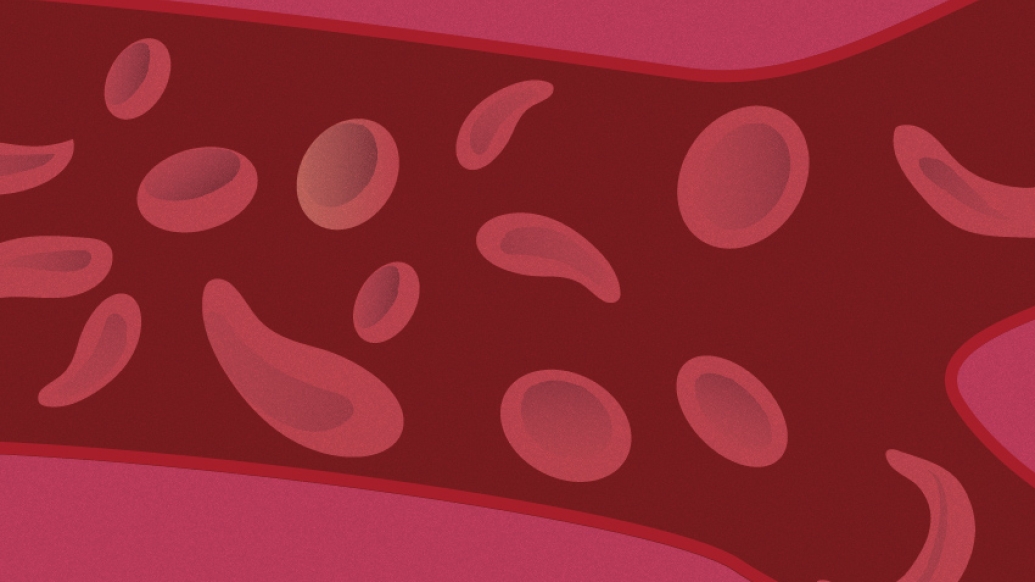
One of the greatest health threats to children with sickle cell anemia is getting a dangerous bacterial infection — but most are not receiving a key medication to reduce the risk, a new study suggests.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
Just 18 percent of children with the inherited blood disease in the Michigan Medicine study received daily antibiotics, according to findings in the journal Pediatrics. Such antibiotic treatment has proved to reduce the risk of infection by 84 percent.
"Most children with sickle cell anemia are not getting the antibiotics they should be to adequately protect against potentially deadly infections," says lead author Sarah Reeves, Ph.D., pediatrics faculty and epidemiologist with the Child Health Evaluation and Research Center at the University of Michigan Medical School and C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
"Long-standing recommendations say children with sickle cell anemia should take antibiotics daily for their first five years of life. It can be lifesaving."
The study involved 2,821 children ages 3 months to 5 years with sickle cell anemia between 2005 and 2012 in Florida, Illinois, Louisiana, Michigan, South Carolina and Texas. Researchers evaluated receipt of antibiotics through insurance claims for filled prescriptions.
Sickle cell, a condition in which irregularly shaped red blood cells prevent adequate oxygen flow throughout the body, is the most common inherited blood disorder. It predominately affects racial and ethnic minority populations in the U.S., with 1 in 375 African-American infants diagnosed with it.
Without intervention, children with the condition are 100 times more likely to get a bacterial infection and 300 times more likely to have a stroke compared with other children. Infections can develop into serious issues such as meningitis or even death.
Doctors need to repeatedly discuss the importance of taking antibiotics with families of children with sickle cell anemia.Sarah Reeves, Ph.D.
Challenges to care
While the study did not examine reasons for the low rate of children with the disease receiving recommended antibiotics, Reeves notes several possible barriers. Caregiver challenges include picking up prescriptions every two weeks from a pharmacy and remembering to administer the antibiotics to a young, healthy-appearing child twice a day.
SEE ALSO: Most Adults Today Say U.S. Children Have Worse Health Prospects
"The types of challenges involved in making sure children get the recommended dose of antibiotics is exacerbated by the substantial burden of care already experienced by families to help control the symptoms of this disease," says Reeves, who is also a member of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
She says further studies should more deeply explore the barriers preventing families from getting antibiotics and potential interventions to improve the rate of children receiving recommended prescriptions. These may include implementing a system within the medical chart to alert health care providers at appointments that antibiotics need to be prescribed and to prompt conversations with families.
"Interventions to improve the receipt of antibiotics among children with sickle cell anemia should include enhanced collaboration between health care providers, pharmacists and families," Reeves says.
"Doctors need to repeatedly discuss the importance of taking antibiotics with families of children with sickle cell anemia. Social factors that may impact receiving filled prescriptions should also be considered, such as the availability of transportation and time to travel to pharmacies to pick up the prescriptions."

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!