Half of suicidal adolescent show viewers in a hospital sample say the controversial television series contributed to their suicide risk, a new report finds.
9:00 AM
Author |

A significant proportion of suicidal teens treated in a psychiatric emergency department said that watching the Netflix series 13 Reasons Why had increased their suicide risk, a University of Michigan study finds.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
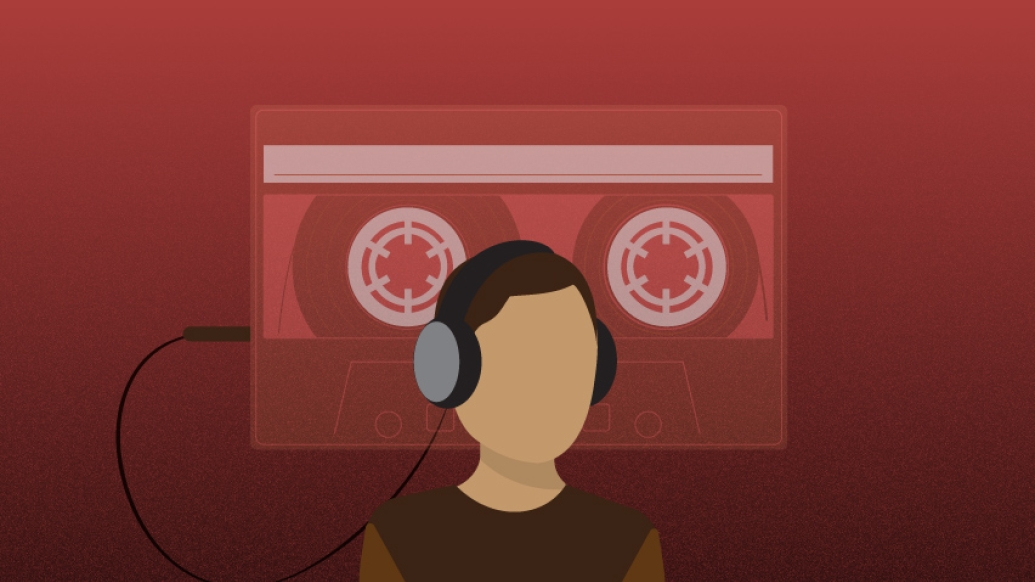
The hit drama, widely popular among teens, has generated controversy for its depiction of suicide. Its story centers around a 17-year-old student, who, before her death, recorded cassettes that detail 13 reasons why she took her own life.
The show has raised concerns among mental health experts about its potentially negative impact on vulnerable youths.
Which is why Michigan Medicine researchers asked suicidal adolescents whether the show had contributed to suicide-related symptoms.
The findings, published in the journal Psychiatric Services, add to the body of literature about how at-risk teens may be reacting to the program.
"This show has been a real phenomenon, especially among teenagers," says lead author Victor Hong, M.D., medical director of psychiatric emergency services at Michigan Medicine. "Its depiction of teen suicide has raised great concern among parents, health providers and educators."
Of the 87 youths who participated in the survey between 2017 and 2018, half had watched at least one episode of the show, mostly teens ages 13 to 17. Among the 43 who had watched it, about half (21) said it heightened their suicide risk.
"Our study doesn't confirm that the show is increasing suicide risk, but it confirms that we should definitely be concerned about its impact on impressionable and vulnerable youth," says Hong.
"Few believe this type of media exposure will take kids who are not depressed and make them suicidal. The concern is about how this may negatively impact youth who are already teetering on the edge."
Parental viewership absent
The idea for the study stemmed from anecdotal narratives shared among colleagues at different children's hospitals, says Hong, noting that providers were hearing more teens being treated for suicidal symptoms talk about 13 Reasons Why.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
The study also found that 84 percent of surveyed youth who had seen the show viewed it alone and were more likely to discuss their reactions with peers (81 percent) than with a parent (35 percent).
A second season of 13 Reasons Why, which debuted in May, opens with a disclaimer urging young viewers to watch the show with a trusted adult — and the importance of seeking help.
Still, very few parents in the U-M sample had watched the series themselves; some were unaware that their child had watched it.
Parents whose kids may be vulnerable or at a high risk for suicide should be even more diligent about what their kids watch and if they are being exposed to content that could trigger them.Cheryl King, Ph.D.
The findings clash with a previous Netflix-commissioned report that found 71 percent of youths in a U.S. community sample talked to a parent about the series.
Hong says this possibly indicates some differences in the ability or desire of youths at high risk of suicide to have such discussions with their parents.
"The data from our sample of teens demonstrated that kids who were at high risk of suicide did not reach out to adults," he adds. "They mostly watched the show alone or talked to friends, but they weren't talking to parents, teachers or school counselors.
"Youths who are in greatest need of adult support may be less likely to seek it out."
Diligence, conversation crucial
Of the teen viewers who said they believed the series increased their suicide risk, the majority strongly identified with the lead female character, Hannah Baker.
"The main character is easy to identify with," Hong says. "She's a teen girl who has suffered from sexual assault, bullying and anxiety — which, unfortunately, impact too many of our youth today."
SEE ALSO: Why Pediatricians Should Screen for Depression in Young Patients
Researchers developed a 44-item questionnaire to assess several aspects of youths' interactions with 13 Reasons Why, using caution to avoid advertising the series to those who were not already aware of it. Teens unfamiliar with the show weren't asked additional questions.
Authors say further research is needed to accurately gauge how media content that focuses on youth suicide can influence the mental health and suicide risk of its viewers.
But in the meantime, there are plenty of red flags for parents to watch for.
"Our findings support the need for tailored prevention programming for vulnerable youths and education and training for their parents," says study senior author Cheryl King, Ph.D., a child and adolescent psychologist at U-M's C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
"Parents whose kids may be vulnerable or at a high risk for suicide should be even more diligent about what their kids watch and if they are being exposed to content that could trigger them," she adds.
"They also shouldn't shy away from open, honest and difficult conversations with their kids about these topics."

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!