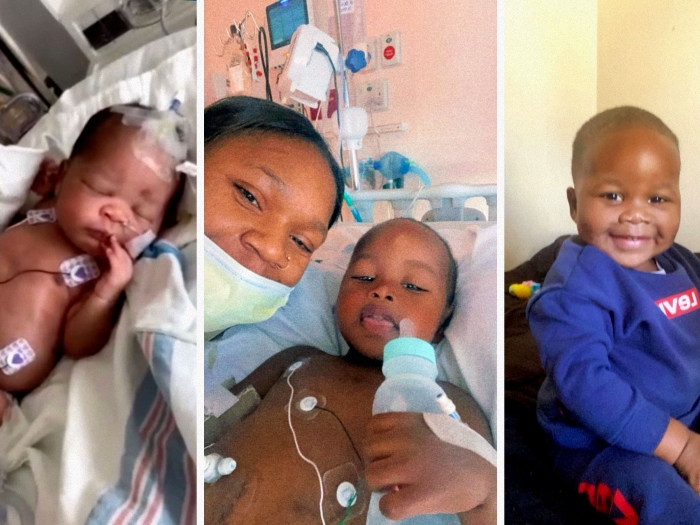
Study suggests that keeping newborns on longer term antiseizure medication may not prevent continued seizures or epilepsy or change development.
2:57 PM
Author |

Newborns who experience seizures after birth are at risk of developing long term chronic conditions, such as developmental delays, cerebral palsy or epilepsy.
Which is why all of these babies receive medication to treat the electrical brain disturbances right away.
While some babies only receive antiseizure medicine for a few days at the hospital, others are sent home with antiseizure medicine for months longer out of concern that seizures may reoccur.
But according to a new multicenter study, continuing this treatment after the neonatal seizures stop may not be necessary.
Babies who stayed on antiseizure medications after going home weren't any less likely to develop epilepsy or to have developmental delays than those who discontinued the medicines before leaving hospital, suggest findings in JAMA Neurology.
"There is wide variability in how different hospitals and physicians manage care for newborns with seizures," says senior author Renée Shellhaas, M.D., M.S., pediatric neurologist at University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital.
Although neonatal seizures usually resolve within 72 hours, longer term medication is often prescribed out of caution, according to co-principal investigator and lead author for the study, Hannah C. Glass, MDCM, MAS.
But "our findings suggest that staying on antiseizure medication after leaving the hospital doesn't protect babies from continued seizures or prevent epilepsy and it does not change developmental outcomes," says Glass, a pediatric neurologist at the University of California, San Francisco Benioff Children's Hospital.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
The study involved about 300 babies born at nine different centers over a three-year period who all developed seizures in their first days to weeks after birth. Two-thirds of babies stayed on medication after discharge from the hospital – averaging four months of treatment. But a third had antiseizure medicine discontinued before they went home – after just a few days of treatment.
We really need to balance the risks of continued medication with benefits to babies' health. If it's not necessary, then keeping them on medicine could do more harm than good.Renée Shellhaas, M.D.
Thirteen percent of babies developed epilepsy but there were no associations with medication duration.
Overmedication risks
Among the biggest concerns for longer term use of antiseizure medicine is that it may expose babies to potentially neurotoxic effects, which research indicates may be associated with lower cognitive scores.
The most commonly used medication for neonatal seizures is phenobarbital, which slows down brain activity but causes sedation.
Newborns who are prescribed this kind of medication for seizures may also have more trouble waking up to feed and engaging in other types of activities important to growth and development.
"We really need to balance the risks of continued medication with benefits to babies' health," Shellhaas says. "If it's not necessary, then keeping them on medicine could do more harm than good."
"Most of the babies in this study went home on antiseizure medications, which suggests we need to re-think standard practice," Glass adds. "We've never had such robust data from multiple centers to support this type of change for newborns with seizures."
Previous small, single-center studies have also suggested that early discontinuation of antiseizure medication isn't harmful.
More than 16,000 newborns in the U.S. experience neonatal seizures each year, with nearly half developing long-term health problems, according to nonprofit organization PCORI, which supported the new study.
Shellhaas, Glass and their colleagues will continue to follow this cohort of infants up to school age to assess development, including sensory processing, IQ and potential learning disabilities through research supported by the National Institutes of Health.
"We want to continue to track these children to watch for any subtle differences that may emerge over time," Shellhaas says.
"We hope this research will help drive decisions about caring for newborns with seizures and help us improve their outcomes over the course of their lives."
Paper Cited: "'Safety of Early Discontinuation of Antiseizure Medication After Acute Symptomatic Neonatal Seizures," JAMA Neurology. DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.1437
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes, Google Podcast or anywhere you listen to podcasts.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!