In type 1 diabetes, new research identifies critical ways to improve blood sugar management across different demographic groups.
10:01 AM
Author |

In the 1990s, a combination of frequent blood sugar monitoring and insulin therapy for individuals with type 1 diabetes was proven to be effective for improving hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels, a measure of average blood sugar, and delaying the onset and progression of diabetes complications.
However, now more than 25 years later, less than a quarter of children and adults achieve the American Diabetes Association goals of HbA1c less than 7% and there are clear disparities in HbA1c outcomes by race, ethnicity and socioeconomic status.
The adoption of the Electronic Health Record in health systems has created an opportunity for improving diabetes care and disparities in outcomes, but what key diabetes self-management behaviors should be measured?
A study of more than 1,200 patients, supported by a collaboration of clinicians and researchers from University of Michigan Health's Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center, the Caswell Diabetes Institute, and Boston's T1D Exchange, validated six critical habits associated with HbA1c that can help reduce disparities in health outcomes for children with type 1 diabetes.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, looked at the association between six key diabetes self-management habits and HbA1c levels in children with type 1 diabetes seen at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital's Pediatric Endocrinology Clinic.
Average HbA1c levels were significantly lower for those that performed one or several of the six habits, which included checking blood sugar levels at least four times a day or using a continuous glucose monitor, given at least three short-acting insulin boluses a day, using an insulin pump, delivering insulin before meals, reviewing blood sugar data since last clinic visit and changing insulin doses since last clinic visit.
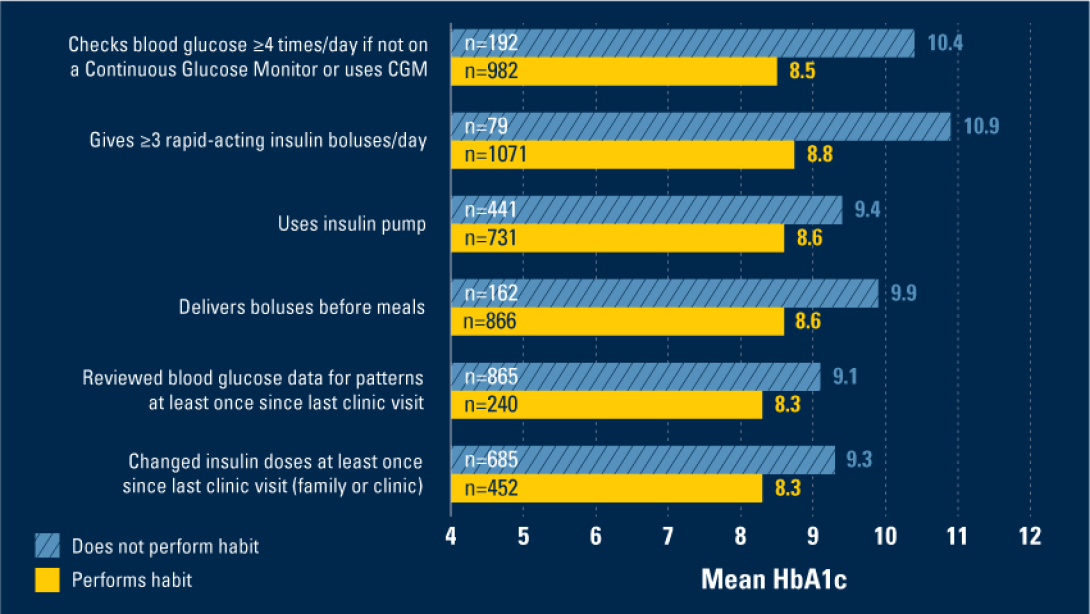
"We calculated a total habit score, which summed all six habits for each individual and found that for every additional habit performed, there was a 0.6% decrease in HbA1c. This relationship between the number of habits and HbA1c persisted across all demographic groups, including age, race, insurance, and parent education," said first author Joyce Lee, M.D., M.P.H., a pediatric endocrinologist and member of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
"Our findings suggest that helping our patients achieve more of these habits will improve their health outcomes and reduce disparities in those outcomes." says Lee. According to the study, less than 9% of the total clinic population performed all six habits, suggesting more work needs to be done to improve diabetes outcomes for pediatric patients.
To make the implementation of documenting these data measures as efficient as possible for providers, Lee, also associate chief medical information officer for pediatric research, created a low-burden, electronic health record workflow at U-M.
"Use of the Electronic Health Record to document these habits is key for improving health outcomes. If you don't record the habits you can't measure them, if you can't measure them you cannot improve on them, and if you can't improve on them, we won't see the full benefits of research discovery and innovation. We owe it to our patients and families to deliver the best high-quality, reliable, and consistent care possible and the Electronic Health Record is critical for helping us achieve this." said Lee.
Paper cited: "Feasibility of Electronic Health Record Assessment of 6 Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes Self-Management Habits and Their Association with Glycemic Outcomes," JAMA Network Open. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.31278
Like Podcasts? Add the Michigan Medicine News Break on iTunes, Google Podcasts or anywhere you listen to podcasts

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!