Approach opens a new avenue to study the biology of acute leukemia and for the development of new drugs.
5:00 AM
Author |
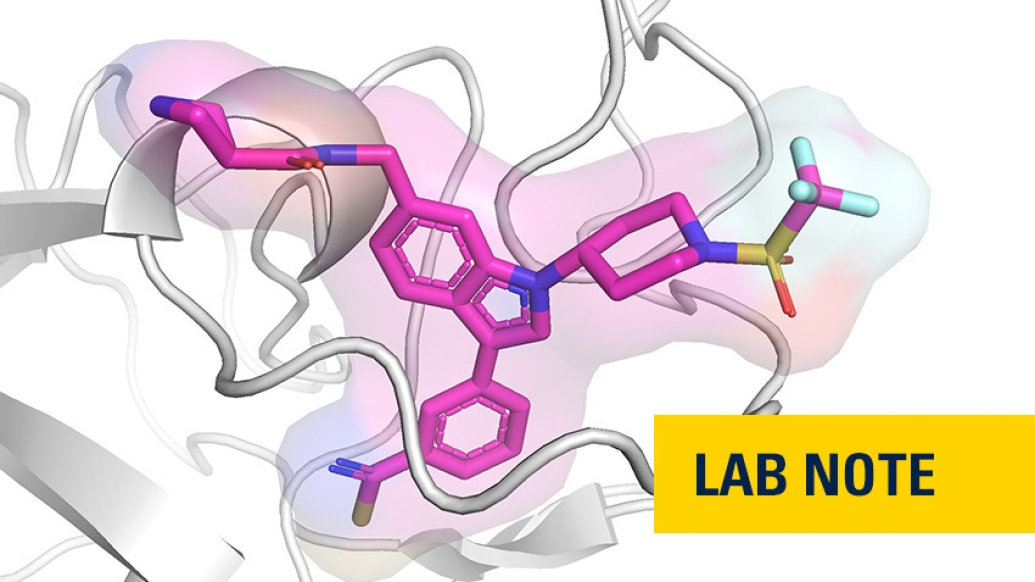
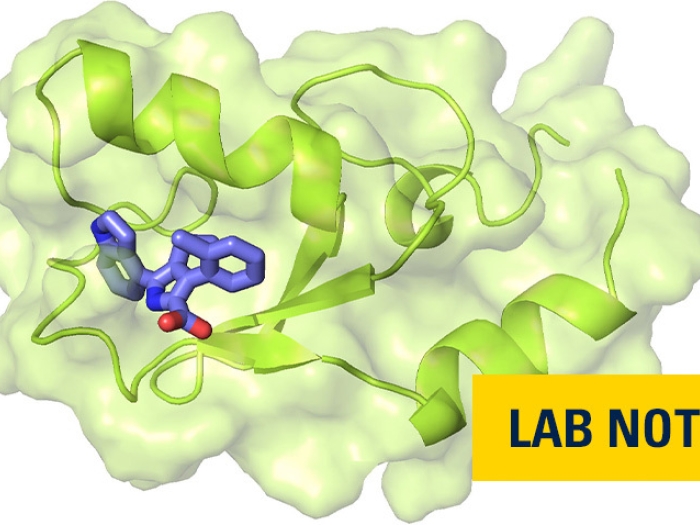
The protein made by the ASH1L gene plays a key role in the development of acute leukemia, along with other diseases. The ASH1L protein, however, has been challenging to target therapeutically.
Now a team of researchers led by Jolanta Grembecka, Ph.D., and Tomasz Cierpicki, Ph.D., from the University of Michigan has developed first-in-class small molecules to inhibit ASH1L's SET domain — preventing critical molecular interactions in the development and progression of leukemia.
The team's findings, which used fragment-based screening, followed by medicinal chemistry and a structure-based design, appear in Nature Communications.
In mouse models of mixed lineage leukemia, the lead compound, known as AS-99, successfully reduced leukemia progression.
"This work points to a new, exiting avenue to develop new therapeutic agents against acute leukemia, as well as providing a new approach to further study the biological functions of ASH1L and its role in the development of the disease," says Grembecka, associate professor of pathology at Michigan Medicine and co-director of the developmental therapeutics program at the U-M Rogel Cancer Center.
The study was a close collaboration between her lab and the lab of co-senior author Cierpicki, an associate professor of biophysics and pathology.
Paper citied: "Discovery of first-in-class inhibitors of ASH1L histone methyltransferase with anti-leukemic activity," Nature Communications. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-23152-6

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!