Studies suggest the gut microbiome can influence immunotherapy side effects. Butyrate emerges as an intriguing candidate against inflammation in the colon.
9:07 AM
Author |
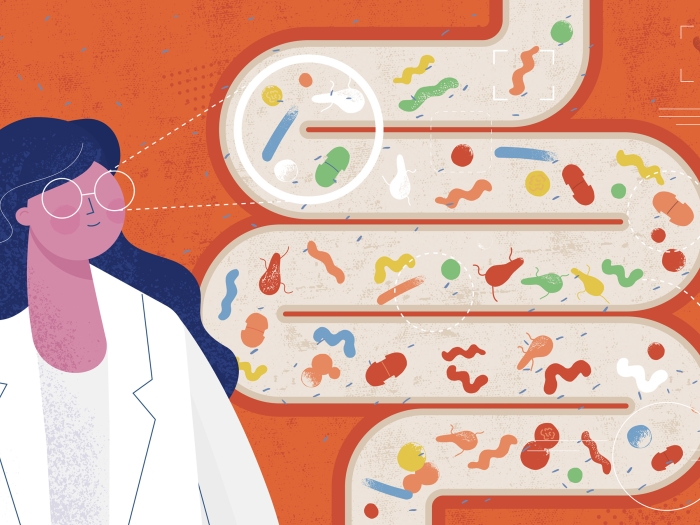
Prebiotics are an intriguing potential approach to curbing some of the severe side effects that life-saving immunotherapy treatments can wreak on the gut, according to an analysis of recent studies and clinical trials by researchers at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center.
Rather than trying to introduce beneficial strains of bacteria directly into a patient's digestive tract — via fecal transplant, enema or probiotic supplements, each of which have drawbacks — evidence points to prebiotics as a potentially safe and effective strategy. This would mean giving patients foods that are known to stimulate the growth of certain bacteria that can, in turn, produce larger amounts of protective metabolites.
"There are several advantages to a prebiotic approach," says hematology/oncology fellow Amy Chang, M.D., the lead author of a recent article on the topic in Trends in Cancer. "Compared to other methods, they're easy to administer, safe and inexpensive. One study showed that oat bran, for example, increased production of a metabolite called butyrate and resulted in improved symptoms for patients with bowel ailments similar to those seen in patients receiving immunotherapy."
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have emerged as a significant advance against a variety of cancer types. But severe side effects — especially inflammation and organ damage caused by the amplification of the body's immune response — can force treatments to be discontinued.
The researchers' review of existing studies and clinical trials raised the possibility that butyrate-promoting prebiotics may help reduce immunotherapy-induced inflammation in the colon, and might even be able to improve the effectiveness of the therapy by increasing patients' tolerance to it through the promotion of beneficial microbes.
The article builds on other research at U-M, including an ongoing clinical trial to explore whether butyrate can help reduce rates of acute graft-versus-host-disease of the intestine, a serious complication of bone marrow transplantation.
"The evidence that exists is compelling, and we believe well-designed clinical trials could help us evaluate the potential of prebiotics to improve outcomes for cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors," says Chang, who worked closely with senior study authors Christopher Lao, M.D., M.P.H. and Muneesh Tewari, M.D., Ph.D., both of whom are members of the Rogel Cancer Center.
The researchers are preparing to open a pilot clinical trial to test a prebiotic dietary supplement in patients receiving immunotherapy.
Paper cited: "Targeting the Gut Microbiome to Mitigate Immunotherapy-Induced Colitis in Cancer," Trends in Cancer. DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2021.02.005

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!