Awareness of genetic testing is low, a new study finds. But an interactive website can help newly diagnosed patients make informed decisions about the practice.
8:00 AM
Author |

Genetic testing after a breast cancer diagnosis can offer clues to individualized treatment decisions for a patient and her treatment team.
But many patients aren't aware it exists and could be missing out on that opportunity, according to a new study published in Cancer.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
A team at the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center recently sought to determine how much newly diagnosed cancer patients understand about the benefits of genetic testing after a diagnosis.
Their other objective: to find out whether a decision support tool would help improve that knowledge.
"After a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer, the relevance of information from genetic testing to her cancer changes," says Michele Gornick, M.A., Ph.D., a researcher at Michigan Medicine and the study's lead author. "The question evolves from: 'Am I going to get breast cancer?' to: 'How likely is it that my cancer comes back — and is my family at higher risk?'"
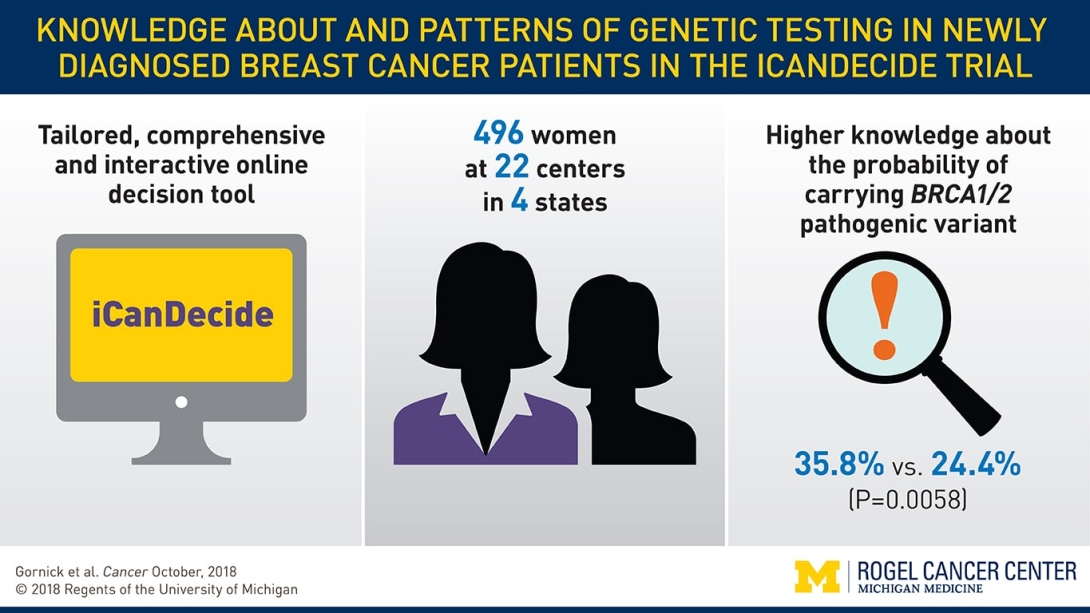
To gain insight, researchers enrolled 496 patients with newly diagnosed early-stage breast cancer from multiple practices in four states. Patients were randomized to view a tailored, interactive decision tool called iCanDecide or similar information on a static website.
The tool, presented as a website, was focused on informing women about their locoregional and systemic treatment. It also had a module about genetic testing that featured information about types of genetic testing, the implications of test results for treatments and the importance of receiving genetic counseling.
Although not a replacement for professional advice, our findings suggest that online tools can provide a useful complement.Sarah T. Hawley, Ph.D., MPH
Tool improves knowledge
About a month after viewing the tool, patients were surveyed to determine their knowledge about genetic testing, including the probability of carrying a BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant, the purposes and benefits of genetic testing, and the implications on cancer recurrence, treatment decisions and family risk.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
Women who used the iCanDecide tool had an 11.4 percent increase in genetic testing knowledge compared with those who did not, researchers found.
Still, overall rates of knowledge in both arms of the study were relatively low.
"Genetics can be hard to understand," Gornick says. "At diagnosis, you have a lot of information coming at you that can be overwhelming. Given this, information shared during counseling may not be adequate.
"Interactive decision tools are one possible way to enhance and improve patients' knowledge."
Genetic counselors crucial
The results underscore the importance of pairing tools like iCanDecide with genetic counseling, which remains a key component of informed decision-making for genetic testing in patients with breast and other cancers, says Sarah T. Hawley, Ph.D., MPH, a professor of internal medicine at Michigan Medicine.
SEE ALSO: Trusted 'Ally': App Guides Breast Cancer Patients Through Treatment
"We need ways and tools to support genetic counselors in helping educate cancer patients and, eventually, their family members," says Hawley, who co-authored the study. "Although not a replacement for professional advice, our findings suggest that online tools can provide a useful complement."
The study also found that fewer than half of the survey respondents reported having a session with a genetic counseling expert.
Ideally, Gornick says, everyone would meet with a genetic counselor. But as the scope of and interest in genetic testing continues to grow, an already scarce genetic counseling workforce is increasingly taxed.
That's why decision support tools offer an opportunity to help oncologists convey important information around the complex breast cancer treatment decision-making process, she says.
This work was funded by a program project grant from the National Cancer Institute (P01 CA163233, Katz).

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!